● Email Deliverability vs Email Delivery
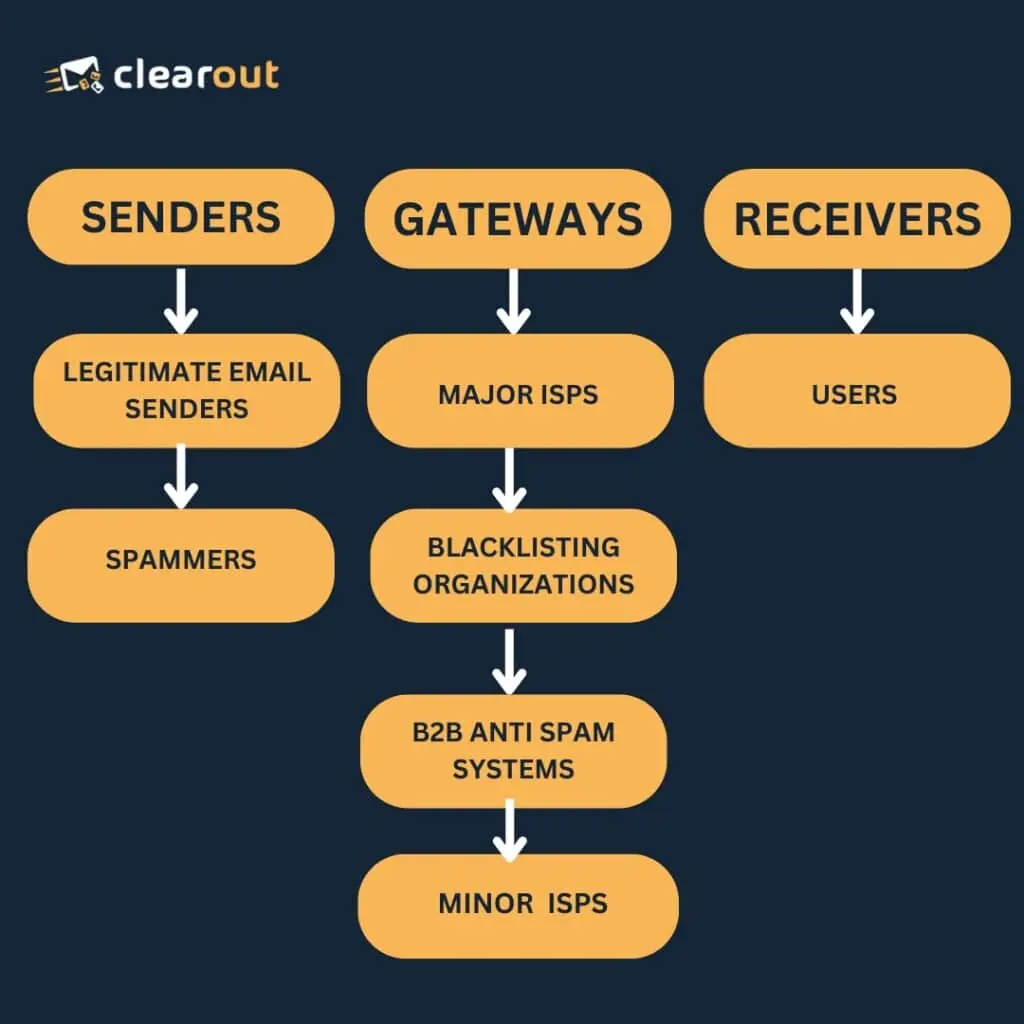
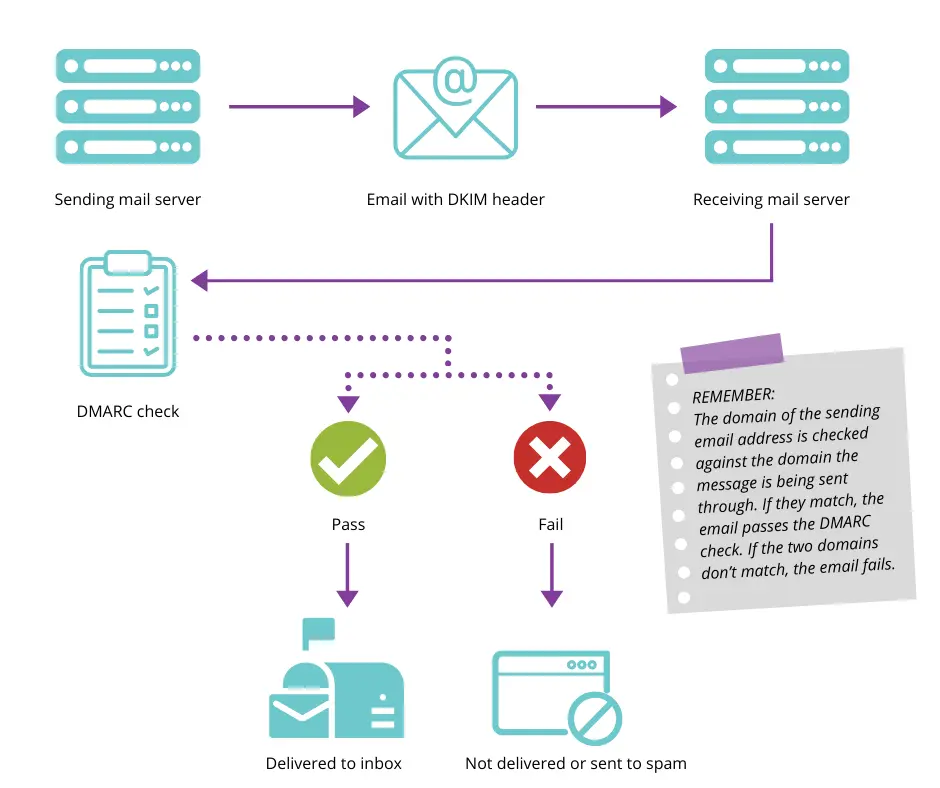
● The Journey of an Email
● Why Maintaining an Email Deliverability Rate Should Be a Priority?
● What is a good email deliverability rate?
● What are the indications of a low email deliverability rate?
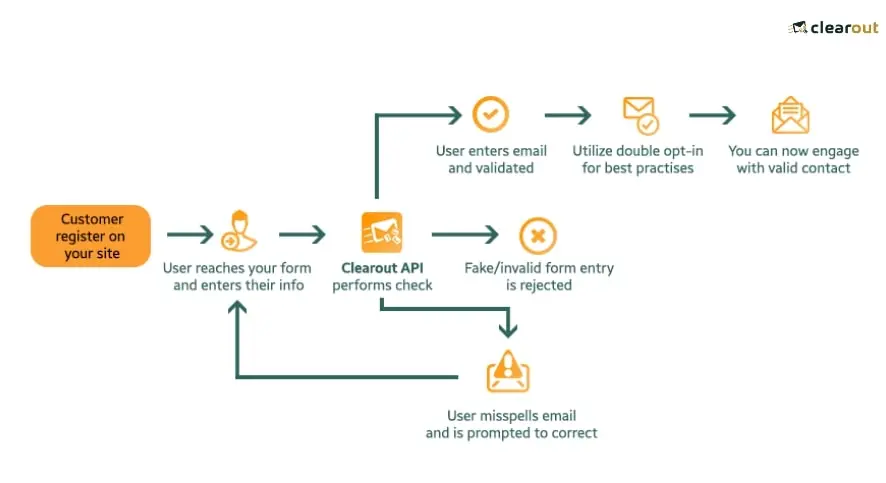
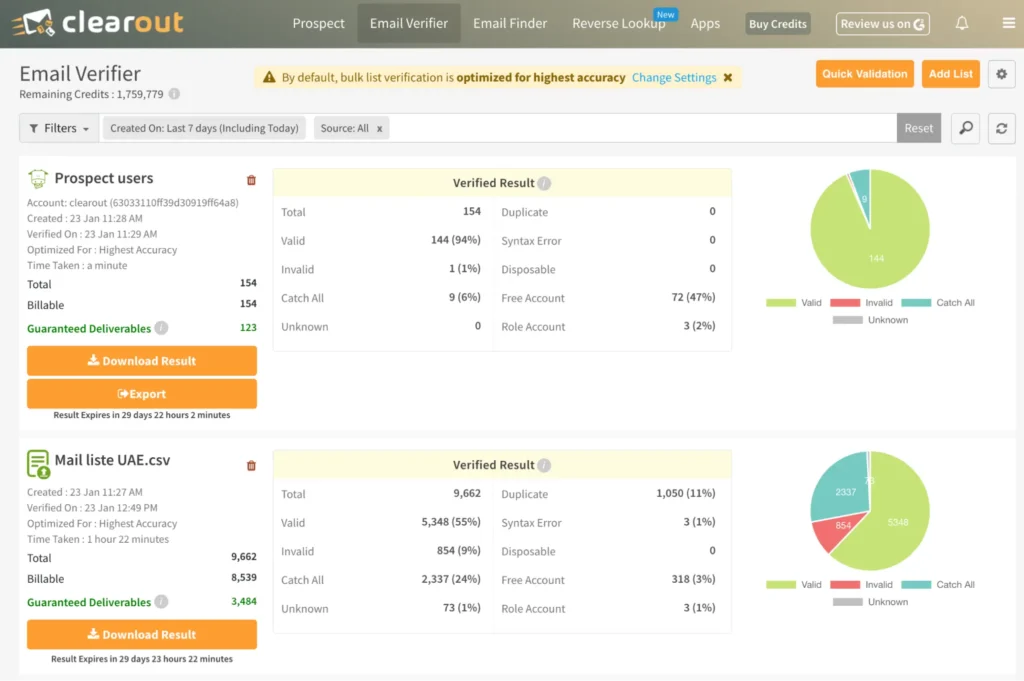
● 13 Factors Affecting Email Deliverability Rate
● Taking the First Step Towards Good Email Deliverability Rate
● The Journey of an Email
● Why Maintaining an Email Deliverability Rate Should Be a Priority?
● What is a good email deliverability rate?
● What are the indications of a low email deliverability rate?
● 13 Factors Affecting Email Deliverability Rate
● Taking the First Step Towards Good Email Deliverability Rate